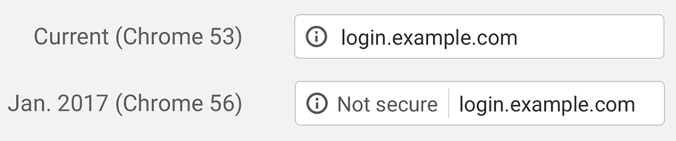
- Trust. If your site is not secure, visitors using version 56 of Chrome (released in January 2017) will see a warning that the site is not secure (see screenshot). Chrome use averages more than 50% of all browser usage. Non-techy visitors (the majority of website users) may become alarmed upon seeing this and leave your site. Alternatively, if your site is secure, this will put them at ease. They may then be more inclined to fill out forms, register or leave comments on your site.
- SEO (search engine optimization). SEO affects where your site falls in search results after someone performs a search. Google has said security will play a part in how they rank sites in search results. For now, it’s a small one. However, if you have a secure site and your competitors don’t, your site could rank higher and give you an edge over them—more people coming across your website. That edge could mean another donation or new member or client for your organization.
- Performance. SSL, which stands for secure socket layer (the means to implement security), can improve page load times. Slow-loading pages cause visitors to become frustrated and leave your site, meaning your organization will miss out on that donation or new member or client.
How Is Security Achieved?
Website security happens when you force HTTPS and obtain and install an SSL certificate.
HTTPS
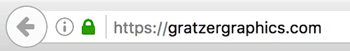
HTTPS (as opposed to just HTTP) encrypts all communication between your visitor’s browser and your website. HTTPS shows up in the browser URL area with a padlock (see screenshot). The difference between HTTPS and HTTP is that with HTTPS the information gets masked by character strings via an SSL certificate. Only the receiving and sending computers can see that information. Others could potentially access it but would not be able to read it.
With a WordPress website, you can use plugins for a DIY approach to HTTPS such as:
SSL Certificate
An SSL certificate is a data file that digitally binds a cryptographic key to an organization’s details. When you install an SSL certificate on your web server, you are allowing for secure connections between a web server and a browser.
You can obtain an SSL certificate from various sources, many free of charge:
You then need to install it, which your web host may do free of charge or for a fee.
What Else?
After taking these steps, you will need to change the URL in your Google Analytics and Search Console accounts to show the HTTPS version.
Conclusion
If you choose to take a do-it-yourself approach to implementing security on your site, note that misconfiguration can result in:
- users not getting to your website;
- images not appearing;
- scripts not loading, affecting functionality on your site;
- your website styles (typography and colors, for example) not displaying properly.
If you need help implementing HTTPS on your site or have any questions: